|
Communication Consultants |
|
Paul Colmer & Associates |



|
Voice over Internet Protocol (Voice over IP, VoIP) is a general term for a family of methodologies, communication protocols, and transmission technologies for delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. Other terms frequently encountered and often used synonymous with VoIP are IP telephony, Internet telephony, voice over broadband (VoBB) and broadband telephony. Internet telephony refers to communications services — voice, fax, SMS, and/or voice-messaging applications — that are transported via the Internet, rather than the public switched telephone network (PSTN). The steps involved in originating an VoIP telephone call are signalling and media channel setup, digitization of the analogue voice signal, optionally compression, packetization, and transmission as Internet Protocol (IP) packets over a packet-switched network. On the receiving side similar steps reproduce the original voice stream. VoIP systems employ session control protocols to control the set-up and tear-down of calls as well as audio codec's which encode speech allowing transmission over an IP network as digital audio via an audio stream. Codec use is varied between different implementations of VoIP (and often a range of codec's are used); some implementations rely on narrowband and compressed speech, while others support high fidelity stereo codec's. |
|
Consumer market A major development that started in 2004 was the introduction of mass-market VoIP services that utilize existing broadband Internet access, by which subscribers place and receive telephone calls in much the same manner as they would via the public switched telephone network (PSTN). Full-service VoIP phone companies provide inbound and outbound service with Direct Inbound Dialling. Phone calls between subscribers of the same provider are usually free or minimal. A VoIP phone is necessary to connect to a VoIP service provider. This can be implemented in several ways. |
|
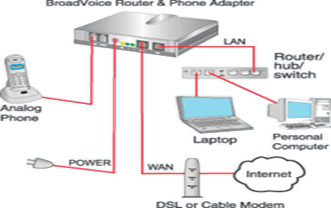
A typical VoIP network setup |
|
· Dedicated VoIP phones connect directly to the IP network using technologies such as wired Ethernet or wireless Wi-Fi. They are typically designed in the style of traditional digital business telephones. · An analogue telephone adapter is a device that connects to the network and implements the electronics and firmware to operate a conventional analogue telephone attached through a modular phone jack. Some residential Internet gateways and cable modems have this function built in. PSTN and mobile network providers
It is becoming increasingly common for telecommunications providers to use VoIP telephony over dedicated and public IP networks to connect switching stations and to interconnect with other telephony network providers; this is often referred to as "IP backhaul". Smart phones and Wi-Fi enabled mobile phones may have SIP clients built into the firmware or available as an application download. Such clients operate independently of the mobile telephone phone network and use either the cellular data connection or WiFi to make and receive phone calls. Corporate use
Because of the bandwidth efficiency and low costs that VoIP technology can provide, businesses are gradually beginning to migrate from traditional copper-wire telephone systems to VoIP systems to reduce their monthly phone costs. VoIP solutions aimed at businesses have evolved into "unified communications" services that treat all communications—phone calls, faxes, voice mail, e-mail, Web conferences and more—as discrete units that can all be delivered via any means and to any handset, including cell phones. Two kinds of competitors are competing in this space: one set is focused on VoIP for medium to large enterprises, while another is targeting the small-to-medium business (SMB) market. VoIP runs both voice and data communications over a single network, which can significantly reduce infrastructure costs. VoIP devices have simple, intuitive user interfaces, so users can often make simple system configuration changes. Dual-mode cell phones enable users to continue their conversations as they move between an outside cellular service and an internal Wi-Fi network, so that it is no longer necessary to carry both a desktop phone and a cell phone. Maintenance becomes simpler as there are fewer devices to oversee. |

|
Home |
|
About Us |
|
Open Source |
|
Service List |
|
Consulting |
|
VOIP |
|
SIP |
|
IAX |
|
H.323 |
|
Network Design |
|
IT Support |
|
Training |
|
Web Design |
|
Product List |
|
Case studies |
|
News Article |
|
Contact Us |